零依赖实现光线追踪算法
光线追踪(Ray Tracing)是计算机图形学中最经典、最优雅的渲染技术之一。它通过模拟光线在场景中的传播过程,能够生成具有真实感的图像——包括精确的阴影、镜面反射、透明折射等效果。从皮克斯的动画电影到如今支持 RTX 的游戏,光线追踪技术无处不在。
本文基于 GAMES101(闫令琪)Lecture 13-14 的内容,从理论到实践,系统介绍光线追踪的核心原理。我们将不依赖任何图形库,仅使用 Python 的基础数学运算,从零实现一个完整的光线追踪渲染器。通过这个case,可以深入理解:
- 光线如何与几何体求交
- Whitted-Style 递归光线追踪的工作原理
- 反射、折射、阴影的数学本质
- 从像素到图像的完整渲染流程
最终,我们将从零开始手写光线追踪算法的实现,不过我的是Python版本,嘿嘿~ 反正原理都一样的
一、为什么需要光线追踪
1.1 光栅化的局限性
光栅化(Rasterization)虽然速度快,适合实时渲染,但在处理以下全局光照效果时存在困难:
- 软阴影(Soft Shadows)
- 光泽反射(Glossy Reflection)- 如金属表面的模糊反射
- 间接光照(Indirect Illumination)- 光线在物体间的多次反弹
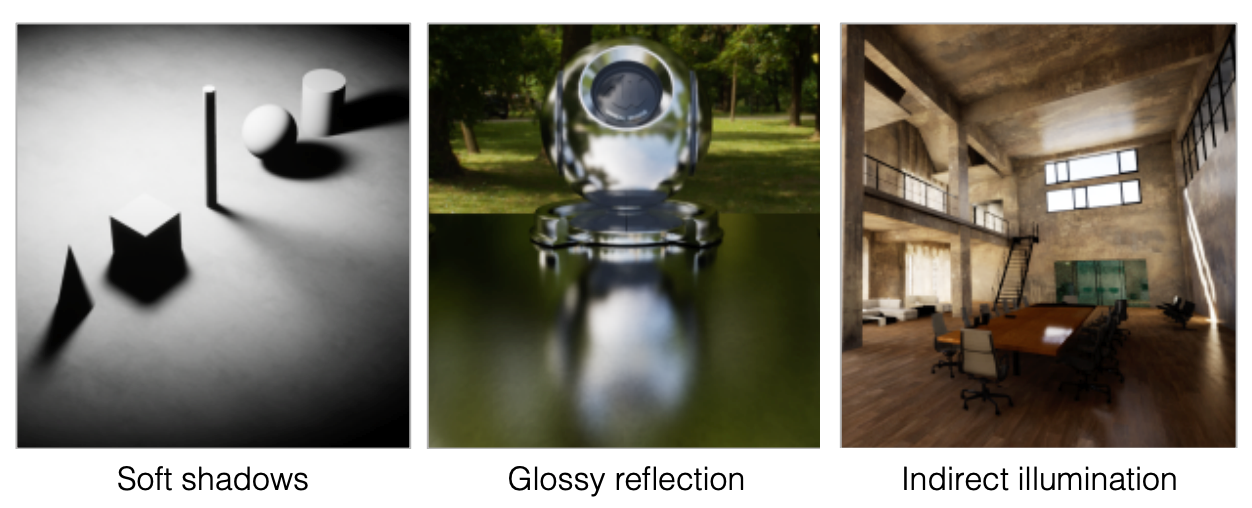

1.2 两种渲染方式对比
| 特性 | 光栅化 | 光线追踪 |
|---|---|---|
| 速度 | 快(实时) | 慢(离线) |
| 质量 | 相对较低 | 高质量 |
| 全局光照 | 难以处理 | 天然支持 |
| 应用场景 | 游戏、实时应用 | 电影、CG动画 |
二、光线的基本定义
2.1 光线的三个假设
- 直线传播:光沿直线传播
- 不发生碰撞:光线之间不会相互影响
- 可逆性(Reciprocity):光路可逆,从光源到眼睛的路径,反过来也成立
2.2 光线的数学表示
光线可以用参数方程表示:
$$ \mathbf{r}(t) = \mathbf{o} + t\mathbf{d}, \quad t \geq 0 $$
其中:
- $\mathbf{o}$:光线起点(Origin)
- $\mathbf{d}$:光线方向(Direction),通常为单位向量
- $t$:参数,表示沿光线方向的距离
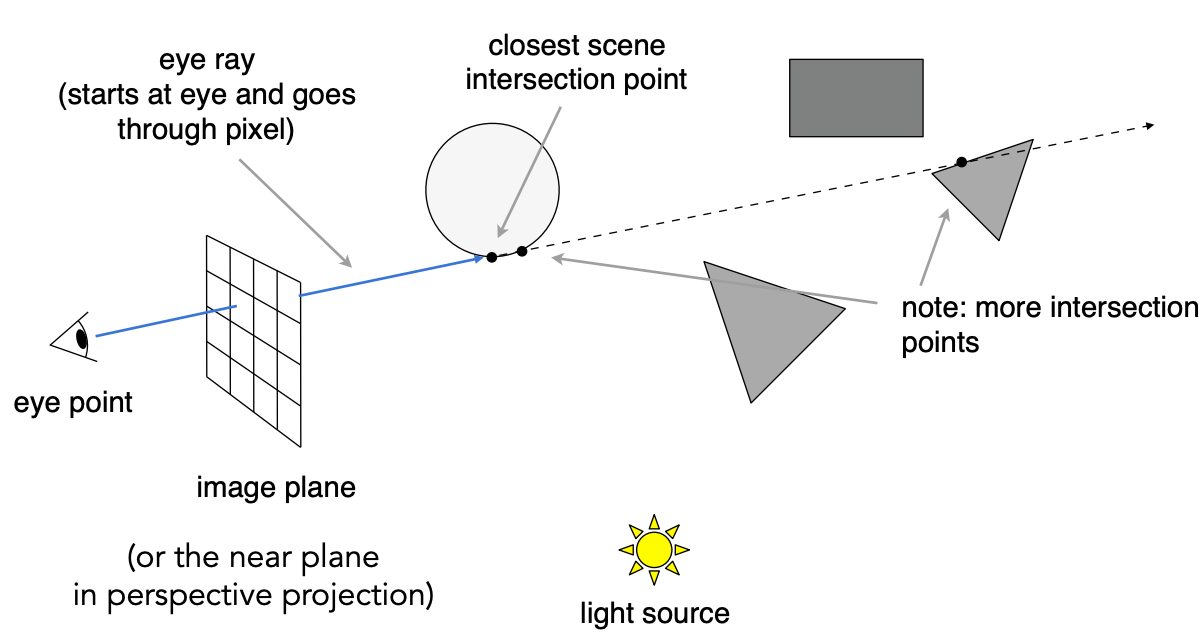
三、光线投射(Ray Casting)
3.1 基本思想
光线投射是光线追踪的基础,其核心步骤:
- 将成像平面划分为像素网格
- 从相机(眼睛)位置,穿过每个像素发射一条光线
- 找到光线与场景中物体的最近交点
- 连接交点与光源,判断是否在阴影中
- 根据光照模型计算该像素的颜色
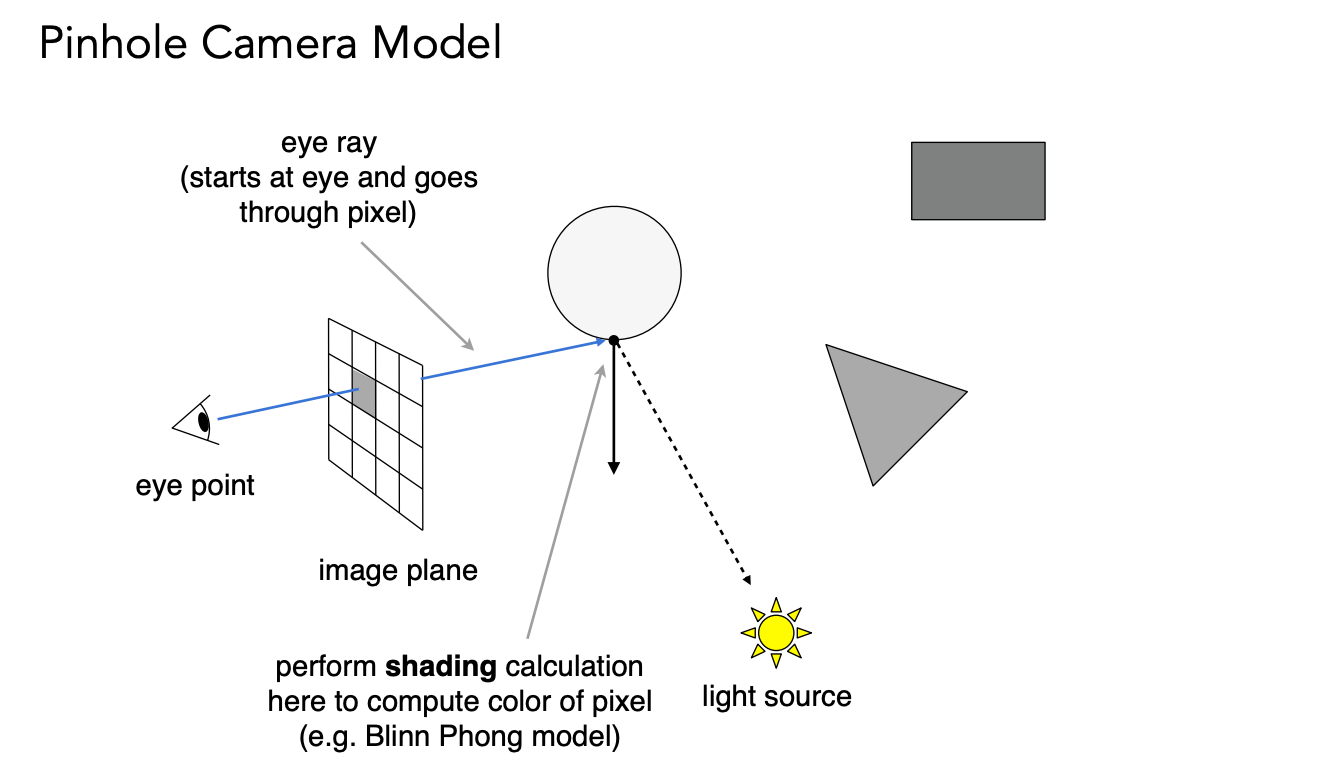
三种光线类型:
- Primary Ray(主光线/Eye Ray):从眼睛出发穿过像素的第一条光线
- Shadow Ray(阴影光线):从交点指向光源,用于判断阴影
- Secondary Ray(次级光线):反射或折射产生的光线
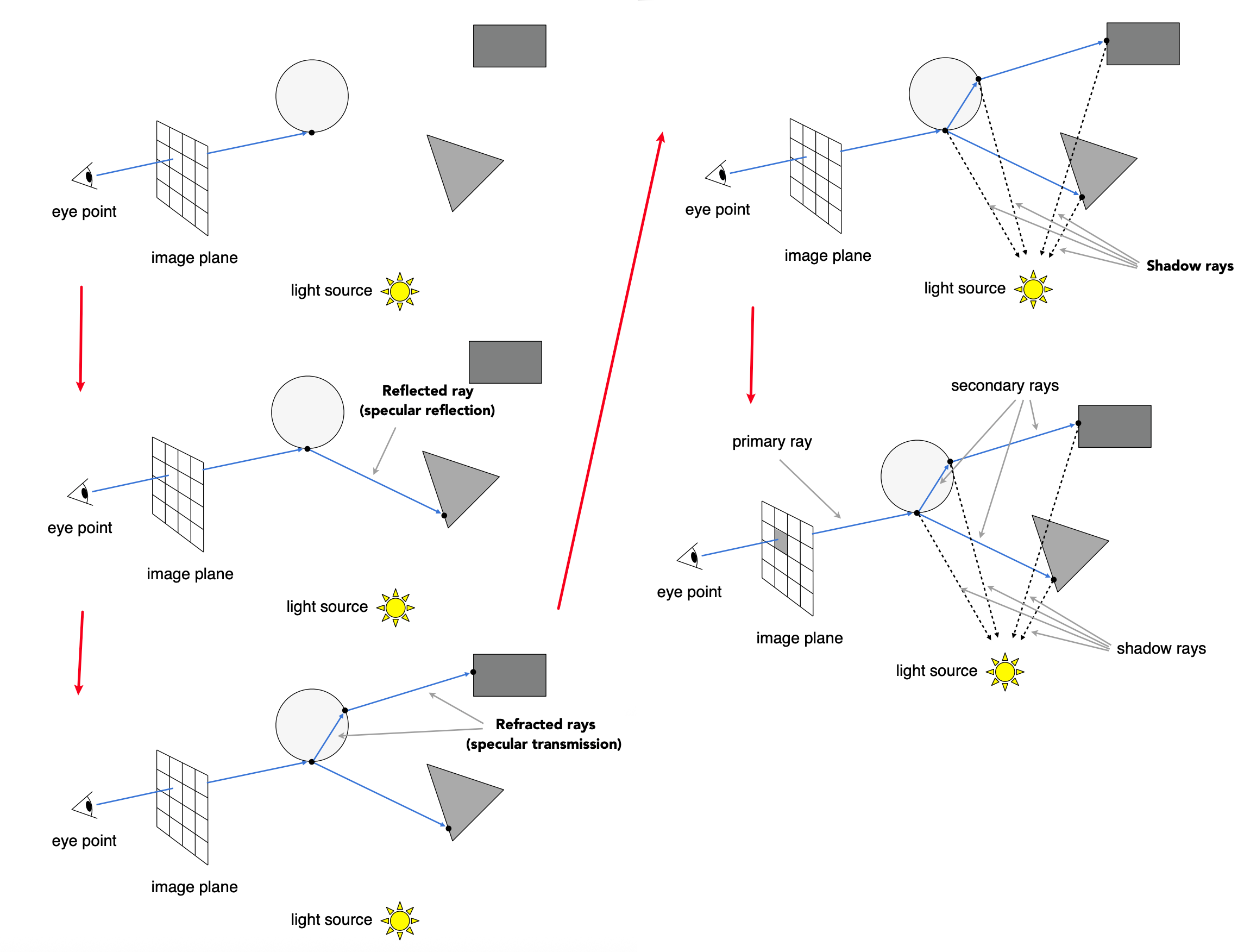
四、Whitted-Style 递归光线追踪
4.1 算法原理
1980年,Turner Whitted 提出了递归光线追踪算法,能够模拟:
- 镜面反射:光线在光滑表面反弹
- 折射:光线穿过透明物体时发生弯曲
- 阴影:物体遮挡光源产生的暗区

4.2 递归过程
当光线击中物体表面时:
- 如果表面是漫反射材质:计算局部光照
- 如果表面是镜面反射材质:生成反射光线,递归追踪
- 如果表面是透明材质:生成折射光线,递归追踪
- 将所有贡献累加得到最终颜色
def cast_ray(origin, direction, depth):
if depth > MAX_DEPTH:
return background_color
hit_point, normal, material = scene_intersect(origin, direction)
if no_intersection:
return background_color
color = Vec3(0, 0, 0)
# 计算局部光照(漫反射 + 高光)
for light in lights:
if not in_shadow(hit_point, light):
color += compute_lighting(hit_point, normal, material, light)
# 反射
if material.is_reflective:
reflect_dir = reflect(direction, normal)
reflect_color = cast_ray(hit_point, reflect_dir, depth + 1)
color += reflect_color * material.reflectivity
# 折射
if material.is_transparent:
refract_dir = refract(direction, normal, material.ior)
refract_color = cast_ray(hit_point, refract_dir, depth + 1)
color += refract_color * material.transparency
return color
五、光线与物体求交
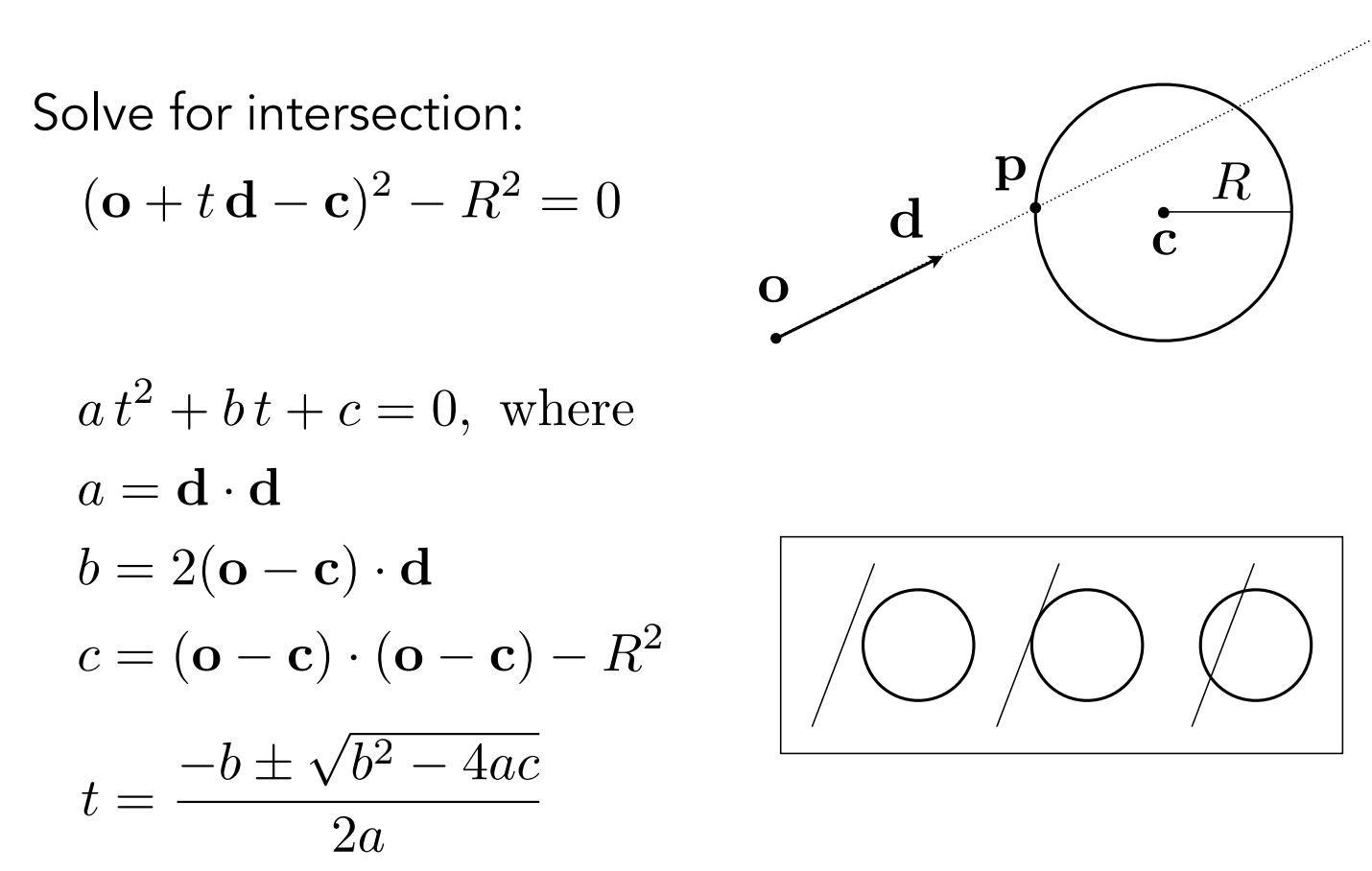
5.1 光线与球体求交
球体方程(圆心 $\mathbf{c}$,半径 $R$):
$$ (\mathbf{p} - \mathbf{c}) \cdot (\mathbf{p} - \mathbf{c}) = R^2 $$
将光线方程 $\mathbf{p} = \mathbf{o} + t\mathbf{d}$ 代入:
$$ (\mathbf{o} + t\mathbf{d} - \mathbf{c}) \cdot (\mathbf{o} + t\mathbf{d} - \mathbf{c}) = R^2 $$
设 $\mathbf{L} = \mathbf{o} - \mathbf{c}$,展开得到二次方程:
$$ (\mathbf{d} \cdot \mathbf{d})t^2 + 2(\mathbf{d} \cdot \mathbf{L})t + (\mathbf{L} \cdot \mathbf{L} - R^2) = 0 $$
即 $at^2 + bt + c = 0$,其中:
- $a = \mathbf{d} \cdot \mathbf{d}$(若 $\mathbf{d}$ 是单位向量则 $a=1$)
- $b = 2(\mathbf{d} \cdot \mathbf{L})$
- $c = \mathbf{L} \cdot \mathbf{L} - R^2$
判别式 $\Delta = b^2 - 4ac$:
- $\Delta < 0$:无交点
- $\Delta = 0$:相切,一个交点
- $\Delta > 0$:两个交点,取较小的正值
def ray_sphere_intersect(origin, direction, center, radius):
L = center - origin
tca = L.dot(direction)
d2 = L.dot(L) - tca * tca
if d2 > radius * radius:
return False, 0
thc = math.sqrt(radius * radius - d2)
t0 = tca - thc
t1 = tca + thc
if t0 < 0:
t0 = t1
if t0 < 0:
return False, 0
return True, t0
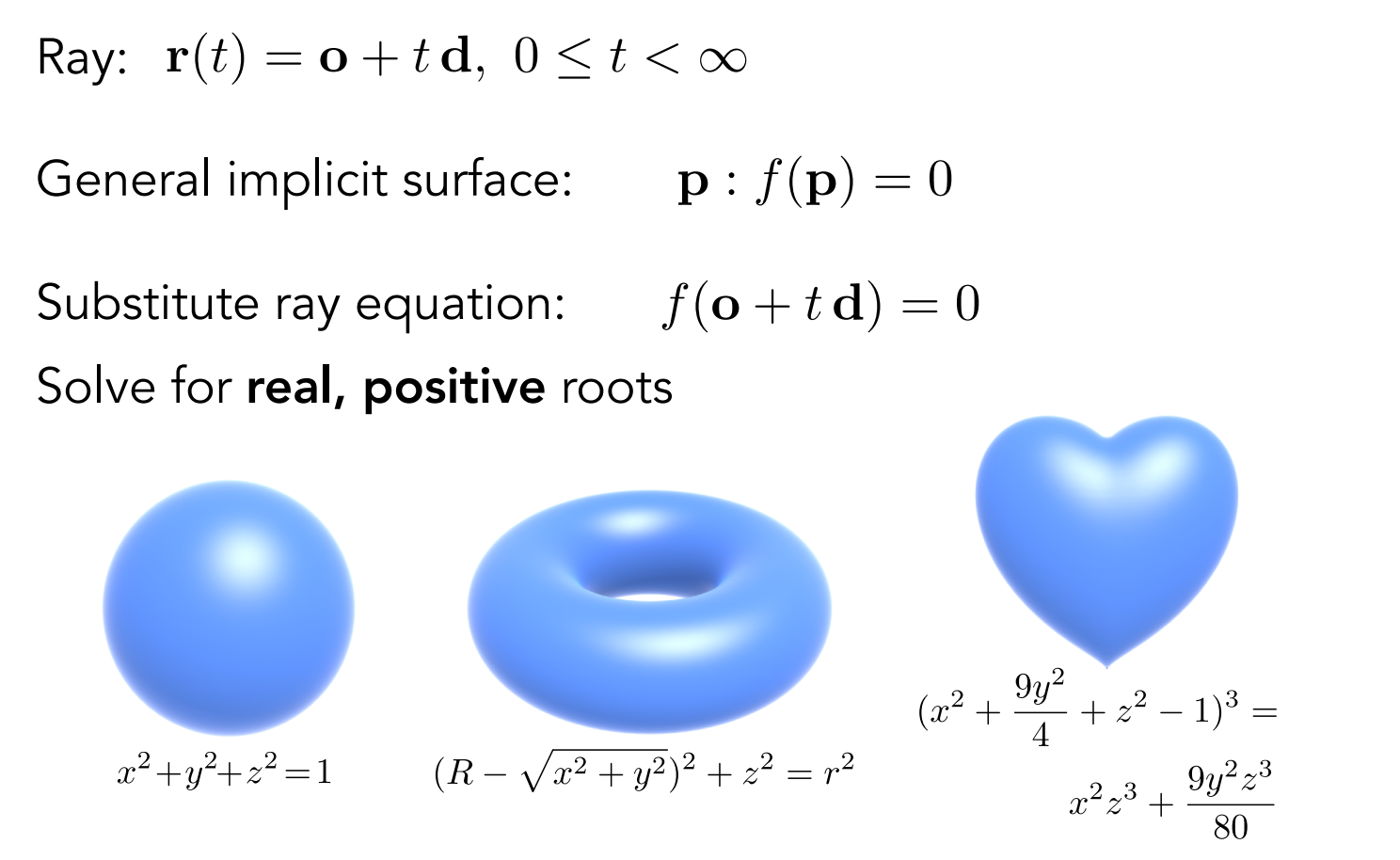
5.2 光线与隐式曲面求交
对于一般隐式曲面 $f(\mathbf{p}) = 0$,将光线方程代入:
$$ f(\mathbf{o} + t\mathbf{d}) = 0 $$
求解 $t$ 的正实根即可。
5.3 光线与三角形求交(Möller-Trumbore 算法)
三角形由三个顶点 $\mathbf{P}_0, \mathbf{P}_1, \mathbf{P}_2$ 定义。三角形内任意一点可用重心坐标表示:
$$ \mathbf{P} = (1 - u - v)\mathbf{P}_0 + u\mathbf{P}_1 + v\mathbf{P}_2 $$
其中 $u \geq 0, v \geq 0, u + v \leq 1$。
将光线方程与重心坐标联立:
$$ \mathbf{o} + t\mathbf{d} = (1-u-v)\mathbf{P}_0 + u\mathbf{P}_1 + v\mathbf{P}_2 $$
整理为矩阵形式:
$$ \begin{bmatrix} -\mathbf{d} & \mathbf{E}_1 & \mathbf{E}_2 \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} t \\ u \\ v \end{bmatrix} = \mathbf{S} $$
其中:
- $\mathbf{E}_1 = \mathbf{P}_1 - \mathbf{P}_0$
- $\mathbf{E}_2 = \mathbf{P}_2 - \mathbf{P}_0$
- $\mathbf{S} = \mathbf{o} - \mathbf{P}_0$
使用 Cramer 法则 求解:
$$ \begin{bmatrix} t \\ u \\ v \end{bmatrix} = \frac{1}{\mathbf{S}_1 \cdot \mathbf{E}_1} \begin{bmatrix} \mathbf{S}_2 \cdot \mathbf{E}_2 \\ \mathbf{S}_1 \cdot \mathbf{S} \\ \mathbf{S}_2 \cdot \mathbf{d} \end{bmatrix} $$
其中:
- $\mathbf{S}_1 = \mathbf{d} \times \mathbf{E}_2$
- $\mathbf{S}_2 = \mathbf{S} \times \mathbf{E}_1$
判断条件:$t > 0$,$u \geq 0$,$v \geq 0$,$u + v \leq 1$
六、光照模型
6.1 漫反射(Lambertian)
漫反射遵循 Lambert 余弦定律:
$$ L_d = k_d \cdot I \cdot \max(0, \mathbf{n} \cdot \mathbf{l}) $$
其中:
- $k_d$:漫反射系数(材质颜色)
- $I$:光源强度
- $\mathbf{n}$:表面法线
- $\mathbf{l}$:指向光源的单位向量
6.2 镜面反射(Blinn-Phong)
$$ L_s = k_s \cdot I \cdot \max(0, \mathbf{n} \cdot \mathbf{h})^p $$
其中:
- $k_s$:镜面反射系数
- $\mathbf{h} = \frac{\mathbf{l} + \mathbf{v}}{|\mathbf{l} + \mathbf{v}|}$:半程向量
- $\mathbf{v}$:指向观察者的单位向量
- $p$:高光指数(Phong 指数)
6.3 反射向量计算
$$ \mathbf{R} = \mathbf{I} - 2(\mathbf{I} \cdot \mathbf{N})\mathbf{N} $$
其中 $\mathbf{I}$ 是入射光线方向,$\mathbf{N}$ 是表面法线。
6.4 折射向量计算(Snell 定律)
$$ \eta_1 \sin\theta_1 = \eta_2 \sin\theta_2 $$
折射向量:
$$ \mathbf{T} = \eta \mathbf{I} + (\eta \cos\theta_1 - \cos\theta_2)\mathbf{N} $$
其中 $\eta = \frac{\eta_1}{\eta_2}$,$\eta_1$ 和 $\eta_2$ 分别是入射介质和折射介质的折射率。
当 $\sin\theta_2 > 1$ 时发生全内反射。
七、阴影检测
从交点向光源发射阴影光线,检测是否有遮挡:
def in_shadow(hit_point, light_position):
shadow_dir = (light_position - hit_point).normalize()
shadow_origin = hit_point + normal * epsilon # 偏移避免自相交
light_distance = (light_position - hit_point).norm()
intersect, shadow_hit, _, _ = scene_intersect(shadow_origin, shadow_dir)
if intersect and (shadow_hit - shadow_origin).norm() < light_distance:
return True # 在阴影中
return False
八、Python 实现要点
8.1 核心数据结构
class Vec3:
"""三维向量:用于点、方向、颜色"""
def __init__(self, x=0, y=0, z=0): ...
def dot(self, other): ... # 点积
def normalize(self): ... # 归一化
def __add__, __sub__, __mul__ # 运算符重载
class Material:
"""材质:颜色、反射率、折射率等"""
diffuse_color: Vec3
albedo: (diffuse, specular, reflect, refract)
specular_exponent: float
refractive_index: float
class Sphere:
"""球体:圆心、半径、材质"""
center: Vec3
radius: float
material: Material
class Light:
"""点光源:位置、强度"""
position: Vec3
intensity: float
8.2 渲染主循环
def render(width, height, fov):
framebuffer = []
for j in range(height):
for i in range(width):
# 计算光线方向
x = (2 * (i + 0.5) / width - 1) * tan(fov/2) * width/height
y = -(2 * (j + 0.5) / height - 1) * tan(fov/2)
direction = Vec3(x, y, -1).normalize()
# 从原点发射光线
color = cast_ray(Vec3(0,0,0), direction, depth=0)
framebuffer.append(color)
return framebuffer
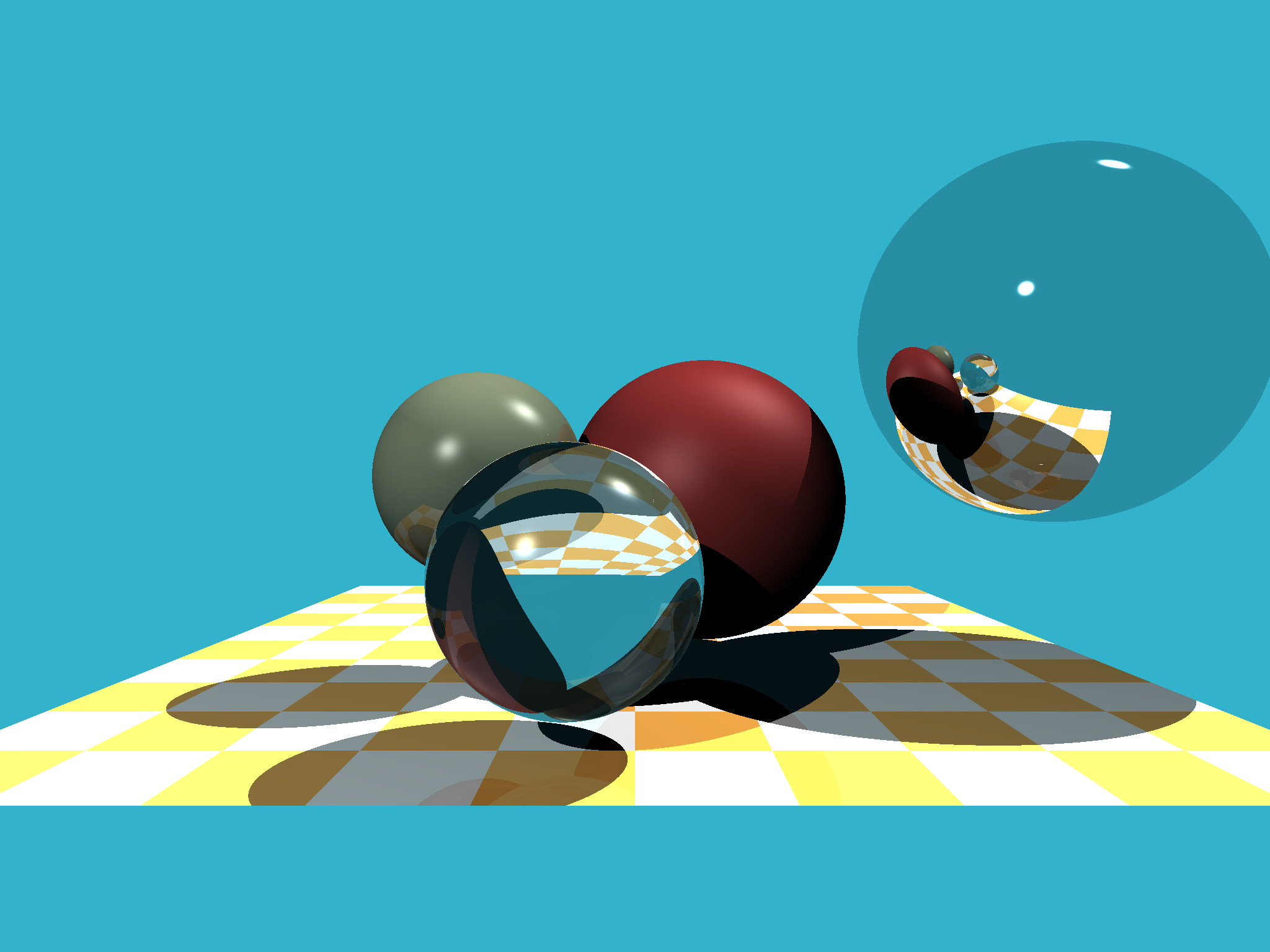
十、运行效果
使用本项目的 raytracer.py,可以渲染出包含以下效果的图像:

- 4个不同材质的球体(象牙、玻璃、橡胶、镜面)
- 多光源照明
- 反射和折射效果
- 阴影
- 棋盘格地板
完整的代码我放这里了:
import math
from typing import List, Tuple
from PIL import Image
class Vec3:
"""三维向量类,用于表示点、方向、颜色等"""
def __init__(self, x: float = 0.0, y: float = 0.0, z: float = 0.0):
self.x = x
self.y = y
self.z = z
def __add__(self, other: 'Vec3') -> 'Vec3':
return Vec3(self.x + other.x, self.y + other.y, self.z + other.z)
def __sub__(self, other: 'Vec3') -> 'Vec3':
return Vec3(self.x - other.x, self.y - other.y, self.z - other.z)
def __mul__(self, scalar: float) -> 'Vec3':
return Vec3(self.x * scalar, self.y * scalar, self.z * scalar)
def __rmul__(self, scalar: float) -> 'Vec3':
return self.__mul__(scalar)
def __neg__(self) -> 'Vec3':
return Vec3(-self.x, -self.y, -self.z)
def dot(self, other: 'Vec3') -> float:
"""点积"""
return self.x * other.x + self.y * other.y + self.z * other.z
def norm(self) -> float:
"""向量的模(长度)"""
return math.sqrt(self.dot(self))
def normalize(self) -> 'Vec3':
"""返回单位向量"""
n = self.norm()
if n < 1e-6:
return Vec3(0, 0, 0)
return self * (1.0 / n)
def __repr__(self) -> str:
return f"Vec3({self.x:.2f}, {self.y:.2f}, {self.z:.2f})"
def reflect(I: Vec3, N: Vec3) -> Vec3:
"""反射向量: I - 2 * (I · N) * N"""
return I - N * 2.0 * I.dot(N)
def refract(I: Vec3, N: Vec3, refractive_index: float) -> Vec3:
"""折射向量(使用斯涅尔定律)"""
cosi = -max(-1.0, min(1.0, I.dot(N)))
etai = 1.0
etat = refractive_index
n = N
if cosi < 0:
cosi = -cosi
etai, etat = etat, etai
n = -N
eta = etai / etat
k = 1 - eta * eta * (1 - cosi * cosi)
if k < 0:
return Vec3(0, 0, 0)
else:
return I * eta + n * (eta * cosi - math.sqrt(k))
class Material:
"""材质类,定义物体表面属性"""
def __init__(self,
diffuse_color: Vec3 = Vec3(1, 1, 1),
albedo: Tuple[float, float, float, float] = (1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0),
specular_exponent: float = 0.0,
refractive_index: float = 1.0):
"""
参数:
diffuse_color: 漫反射颜色
albedo: (漫反射, 镜面反射, 反射, 折射) 权重
specular_exponent: 镜面反射指数(高光强度)
refractive_index: 折射率
"""
self.diffuse_color = diffuse_color
self.albedo = albedo
self.specular_exponent = specular_exponent
self.refractive_index = refractive_index
class Sphere:
"""球体类"""
def __init__(self, center: Vec3, radius: float, material: Material):
self.center = center
self.radius = radius
self.material = material
def ray_intersect(self, orig: Vec3, dir: Vec3) -> Tuple[bool, float]:
"""
射线与球体相交检测
返回: (是否相交, 交点距离)
"""
L = self.center - orig
tca = L.dot(dir)
d2 = L.dot(L) - tca * tca
if d2 > self.radius * self.radius:
return False, 0.0
thc = math.sqrt(self.radius * self.radius - d2)
t0 = tca - thc
t1 = tca + thc
if t0 < 0:
t0 = t1
if t0 < 0:
return False, 0.0
return True, t0
class Light:
"""点光源类"""
def __init__(self, position: Vec3, intensity: float = 1.0):
self.position = position
self.intensity = intensity
def scene_intersect(orig: Vec3, dir: Vec3, spheres: List[Sphere]) -> Tuple[bool, Vec3, Vec3, Material]:
"""
检测射线与场景的交点
返回: (是否相交, 交点位置, 法线, 材质)
"""
spheres_dist = float('inf')
hit = Vec3()
N = Vec3()
material = Material()
# 检测与所有球体的相交
for sphere in spheres:
intersect, dist = sphere.ray_intersect(orig, dir)
if intersect and dist < spheres_dist:
spheres_dist = dist
hit = orig + dir * dist
N = (hit - sphere.center).normalize()
material = sphere.material
# 添加棋盘地板
checkerboard_dist = float('inf')
if abs(dir.y) > 1e-3:
d = -(orig.y + 4) / dir.y # 地板在 y = -4
pt = orig + dir * d
if d > 0 and abs(pt.x) < 10 and pt.z < -10 and pt.z > -30 and d < spheres_dist:
checkerboard_dist = d
hit = pt
N = Vec3(0, 1, 0)
# 棋盘格纹理
color = Vec3(1, 1, 1) if (int(0.5 * hit.x + 1000) + int(0.5 * hit.z)) & 1 else Vec3(1, 0.7, 0.3)
material.diffuse_color = color
material.albedo = (0.6, 0.3, 0.1, 0.0)
material.specular_exponent = 50.0
return min(spheres_dist, checkerboard_dist) < 1000, hit, N, material
def cast_ray(orig: Vec3, dir: Vec3, spheres: List[Sphere], lights: List[Light], depth: int = 0) -> Vec3:
"""
发射光线并计算颜色
depth: 递归深度(用于反射和折射)
"""
intersect, point, N, material = scene_intersect(orig, dir, spheres)
if depth > 4 or not intersect:
# 背景色(渐变)
return Vec3(0.2, 0.7, 0.8)
# 计算反射方向
reflect_dir = reflect(dir, N).normalize()
# 计算折射方向
refract_dir = refract(dir, N, material.refractive_index).normalize()
# 稍微偏移以避免自相交
reflect_orig = point + N * 1e-3 if reflect_dir.dot(N) > 0 else point - N * 1e-3
refract_orig = point - N * 1e-3 if refract_dir.dot(N) < 0 else point + N * 1e-3
# 递归计算反射和折射颜色
reflect_color = cast_ray(reflect_orig, reflect_dir, spheres, lights, depth + 1)
refract_color = cast_ray(refract_orig, refract_dir, spheres, lights, depth + 1)
# 计算光照
diffuse_light_intensity = 0.0
specular_light_intensity = 0.0
for light in lights:
light_dir = (light.position - point).normalize()
light_distance = (light.position - point).norm()
# 阴影检测
shadow_orig = point + N * 1e-3 if light_dir.dot(N) > 0 else point - N * 1e-3
shadow_intersect, shadow_pt, _, _ = scene_intersect(shadow_orig, light_dir, spheres)
if shadow_intersect and (shadow_pt - shadow_orig).norm() < light_distance:
continue # 在阴影中
# 漫反射(Lambert 余弦定律)
diffuse_light_intensity += light.intensity * max(0.0, light_dir.dot(N))
# 镜面反射(Blinn-Phong 模型)
specular_light_intensity += math.pow(
max(0.0, -reflect(-light_dir, N).dot(dir)),
material.specular_exponent
) * light.intensity
# 组合所有光照分量
color = (material.diffuse_color * diffuse_light_intensity * material.albedo[0] +
Vec3(1, 1, 1) * specular_light_intensity * material.albedo[1] +
reflect_color * material.albedo[2] +
refract_color * material.albedo[3])
return color
def render(spheres: List[Sphere], lights: List[Light], width: int = 1024, height: int = 768) -> List[Vec3]:
"""
渲染场景
返回: 颜色数组
"""
fov = math.pi / 3.0 # 视场角 60 度
framebuffer = []
for j in range(height):
for i in range(width):
# 计算射线方向
x = (2 * (i + 0.5) / width - 1) * math.tan(fov / 2.0) * width / height
y = -(2 * (j + 0.5) / height - 1) * math.tan(fov / 2.0)
dir = Vec3(x, y, -1).normalize()
# 从原点发射射线
framebuffer.append(cast_ray(Vec3(0, 0, 0), dir, spheres, lights))
# 显示进度
if (j + 1) % 50 == 0:
print(f"渲染进度: {(j + 1) / height * 100:.1f}%")
return framebuffer
def save_png(filename: str, framebuffer: List[Vec3], width: int, height: int):
"""保存为 PNG 格式图像(使用 Pillow)"""
if Image is None:
print(f"跳过保存 {filename}: 需要安装 Pillow 库")
return
# 创建 RGB 图像
img = Image.new('RGB', (width, height))
pixels = []
for color in framebuffer:
# 限制颜色范围在 [0, 1] 并转换为 [0, 255]
r = max(0, min(255, int(255 * color.x)))
g = max(0, min(255, int(255 * color.y)))
b = max(0, min(255, int(255 * color.z)))
pixels.append((r, g, b))
img.putdata(pixels)
img.save(filename)
print(f" ✓ {filename}")
def main():
"""主函数 - 创建场景并渲染"""
# 定义材质
ivory = Material(
diffuse_color=Vec3(0.4, 0.4, 0.3),
albedo=(0.6, 0.3, 0.1, 0.0),
specular_exponent=50.0
)
glass = Material(
diffuse_color=Vec3(0.6, 0.7, 0.8),
albedo=(0.0, 0.5, 0.1, 0.8),
specular_exponent=125.0,
refractive_index=1.5
)
red_rubber = Material(
diffuse_color=Vec3(0.3, 0.1, 0.1),
albedo=(0.9, 0.1, 0.0, 0.0),
specular_exponent=10.0
)
mirror = Material(
diffuse_color=Vec3(1.0, 1.0, 1.0),
albedo=(0.0, 10.0, 0.8, 0.0),
specular_exponent=1425.0
)
# 创建球体
spheres = [
Sphere(Vec3(-3, 0, -16), 2, ivory),
Sphere(Vec3(-1.0, -1.5, -12), 2, glass),
Sphere(Vec3(1.5, -0.5, -18), 3, red_rubber),
Sphere(Vec3(9, 3, -18), 4, mirror)
]
# 创建光源
lights = [
Light(Vec3(-20, 20, 20), 1.5),
Light(Vec3(30, 50, -25), 1.8),
]
# 渲染设置
width = 2048
height = 1536
print("开始渲染...")
print(f"分辨率: {width}x{height}")
print(f"球体数量: {len(spheres)}")
print(f"光源数量: {len(lights)}")
print()
# 渲染场景
framebuffer = render(spheres, lights, width, height)
# 保存图像
print("\n保存图像...")
save_png("output.png", framebuffer, width, height)
print("\n完成!")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
参考资料
- GAMES101: 现代计算机图形学入门 - 闫令琪
- TinyRaytracer - Dmitry V. Sokolov